Health experts are issuing urgent guidance on how to effectively eliminate scabies from homes and prevent its spread, as cases of this highly contagious skin condition have surged dramatically in recent years. According to data reported by The Guardian, infections increased by a staggering 44 per cent between 2023 and 2024, highlighting a growing public health concern that requires immediate attention and proper management strategies.
Understanding the Scabies Parasite and Its Symptoms
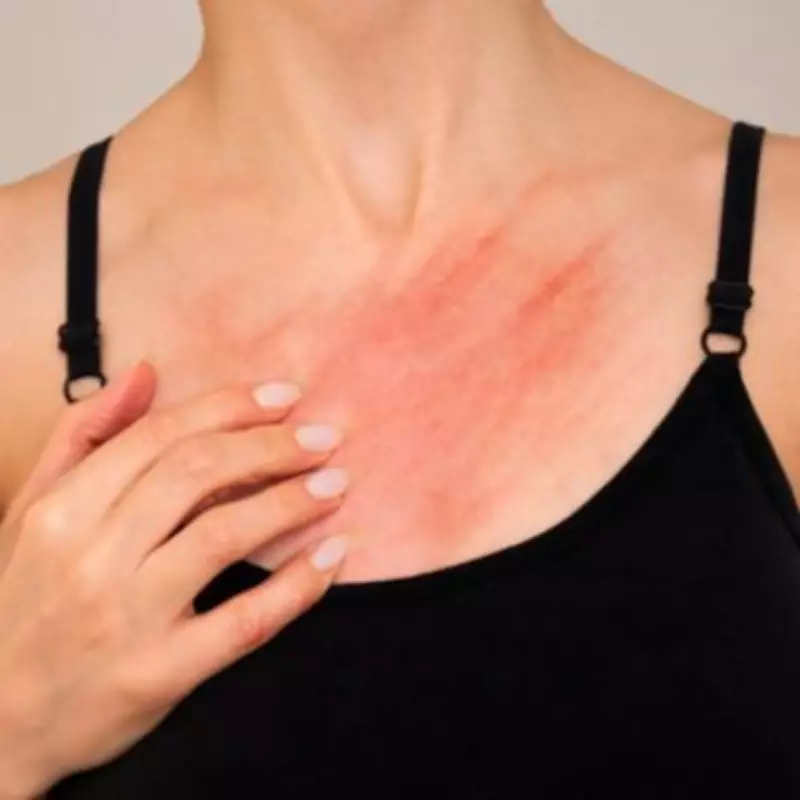
Scabies is caused by the microscopic scabies mite, a tiny parasite measuring just 0.5mm or less that burrows into the top layer of human skin. Unlike bedbugs, which can grow up to 7mm and are visible to the naked eye, these mites are virtually invisible without magnification. They create distinctive linear burrows where they lay eggs that develop into adult mites within one to two weeks, continuing the infestation cycle.
Many infected individuals experience no symptoms during the initial four to six weeks after infestation, as the body takes time to develop an allergic reaction to the mite proteins and their droppings. Once symptoms appear, they typically include:
- Severe itching that intensifies at night when skin temperature rises and mites become more active
- A rash featuring tiny raised linear burrows and small red bumps
- Affected areas commonly include fingers, wrists, arms, armpits, legs, and the groin region
How Scabies Spreads and Who Is Most Vulnerable
The condition primarily transmits through direct, prolonged skin-to-skin contact with an infected person, making household members, particularly those sharing beds, especially vulnerable. The British Association of Dermatologists emphasizes that scabies has no connection to personal hygiene or home cleanliness, countering common misconceptions about the condition.
Outbreaks frequently occur in environments where close contact is unavoidable, including:
- Nurseries, playgroups, and schools where children interact closely
- Residential care homes with communal living arrangements
- Households with multiple occupants sharing living spaces
Seasonal patterns also influence transmission rates, with cooler winter temperatures allowing mites to survive longer away from their human hosts, potentially contributing to increased spread during colder months.
Effective Treatment Protocols for Scabies Infection
Medical professionals recommend a two-pronged approach to scabies treatment, beginning with topical applications before progressing to oral medications if necessary. Permethrin cream serves as the standard first-line treatment available through pharmacies without prescription.
Crucial treatment principles include:
- Simultaneous treatment of all household members, regardless of whether symptoms are present
- Repeat applications to eliminate newly hatched mites and break the reproductive cycle
- Consultation with a GP for Ivermectin prescription if Permethrin proves ineffective, with dosage carefully calibrated according to body weight
Comprehensive Home Cleaning Strategy
While scabies mites typically survive only about three days away from human skin, proper home cleaning remains essential to prevent reinfection. Natalie Bungay of the British Pest Control Association provides specific recommendations for dealing with potentially contaminated household items.
For bedding, towels, and clothing:
- Wash all items that have contacted infected skin at 50°C or higher
- Avoid 30°C cycles as scabies eggs can survive these temperatures
- Dry thoroughly using hot dryer cycles or sunlight exposure, as UV light helps eliminate parasites
- Seal non-washable items like duvets or overcoats in plastic bags for at least one week
For mattresses and upholstered furniture:
- Vacuum all sides and seams of mattresses thoroughly
- Use plastic mattress covers as protective barriers
- Clean sofas and armchairs completely with vacuum attachments
- Dispose of vacuum contents immediately in outdoor bins and wash reusable parts with hot water
This comprehensive approach combining medical treatment with thorough environmental cleaning offers the most effective strategy for eliminating scabies infestations and preventing their spread within communities. As cases continue to rise, understanding proper management techniques becomes increasingly vital for public health protection.





